Which of the following is True of Internet-of-Things Devices speaks for a groundbreaking shift in how technology interweaves with daily life. This interconnected web of devices transcends traditional boundaries, embedding intelligence into our environment and revolutionizing numerous industries. Understanding the veracity of statements surrounding IoT devices necessitates a deep dive into their functionality, benefits, security implications, and transformative potential.
Functionality of IoT Devices
IoT devices operate through synergistic sensors, actuators, and a network of communication protocols. These components collectively enable devices to gather data, process information, and execute commands autonomously or with minimal human intervention. The operational framework of IoT devices hinges on their ability to communicate seamlessly across diverse platforms, leveraging technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and, more recently, 5G. This capability allows for real-time data exchange, fostering environments where devices can ‘talk’ to each other, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
Benefits of IoT Devices
The proliferation of IoT devices brings many benefits spanning various sectors. IoT facilitates remote patient monitoring in healthcare, enabling continuous health data collection and proactive medical interventions. Industrial sectors benefit from predictive maintenance and asset tracking, which reduce downtime and optimize operational efficiency. Smart homes leverage IoT to provide enhanced security, energy management, and convenience, creating a personalized living experience. The ability of IoT devices to streamline processes, reduce human error, and provide actionable insights underscores their value proposition in contemporary society.
Security Challenges of IoT Devices
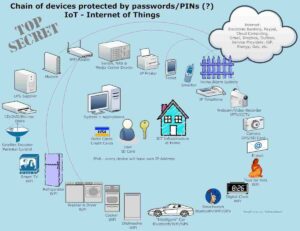
Despite their myriad benefits, IoT devices pose significant security challenges. The extensive connectivity that defines IoT ecosystems creates numerous entry points for cyber threats. Vulnerabilities in device firmware, insufficient encryption, and lack of standardized security protocols expose IoT networks to potential breaches. The implications of compromised IoT devices are far-reaching, ranging from privacy invasions to large-scale disruptions in critical infrastructure. Ensuring robust security measures, such as implementing end-to-end encryption, regular firmware updates, and employing IoT-specific security frameworks, is paramount to safeguarding these devices.
Transformative Impact on Industries of Which of the following is True of Internet-of-Things Devices
IoT devices are at the forefront of digital transformation across various industries. In agriculture, IoT-enabled sensors monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, enabling precision farming and sustainable practices. The logistics sector benefits from real-time tracking of goods, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing losses. In urban planning, innovative city initiatives utilize IoT to manage traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance public safety. The pervasive influence of IoT extends to environmental monitoring, where devices collect critical data on air quality, water levels, and wildlife habitats, informing conservation efforts and policy-making.
Future Prospects of IoT Devices
The prospects of IoT devices are vast and promising, poised to usher in an era of unprecedented innovation and connectivity. As technology advances, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with IoT will enhance the analytical capabilities of these devices, allowing for more sophisticated decision-making processes and predictive analytics. This convergence will enable IoT systems to learn from data patterns, anticipate needs, and autonomously optimize operations, further embedding intelligence into the fabric of everyday life.
IoT in Healthcare
One of the most impactful areas for future IoT development is healthcare. IoT devices, combined with wearable technology, will enable continuous health monitoring, providing real-time data to healthcare providers and allowing personalized treatment plans. Advanced IoT solutions will facilitate remote surgeries through robotic systems, telemedicine, and improved management of chronic diseases. This will guide to better patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and increased accessibility to medical services, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
IoT and Smart Cities
IoT innovations will significantly propel the concept of smart cities. IoT devices will manage urban infrastructure efficiently, from smart grids that optimize energy consumption to intelligent transportation systems that reduce traffic crowding and emissions. Public safety will be enhanced through IoT-based surveillance and emergency response systems. Moreover, IoT will play a critical role in waste management, water supply, and environmental conservation, contributing to sustainable urban development and improved quality of life for residents.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the immense potential, the proliferation of IoT devices brings challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed. Data privacy is a paramount concern, as the vast amounts of personal data collected by IoT devices can be susceptible to misuse. Establishing stringent data protection regulations and ensuring transparent data handling practices will be crucial. Additionally, the ethical implications of autonomous IoT systems, particularly in healthcare and security, require careful consideration to prevent unintended consequences and ensure that these technologies serve the public good.
Regulatory and Standardization Efforts
To fully notice the potential of IoT devices, regulatory and standardization efforts must keep pace with technological advancements. Developing comprehensive standards for IoT security, interoperability, and data privacy will be essential in fostering a trustworthy IoT ecosystem. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders, governments, and international organizations will be needed to create a cohesive framework that supports innovation while safeguarding against risks.
Conclusion
The journey of Which of the following is True of Internet-of-Things Devices from nascent technology to ubiquitous presence highlights their transformative power and the complexities they introduce. As IoT continues to evolve, it will redefine industries, enhance everyday experiences, and drive the next wave of technological revolution. Embracing this future requires a balanced approach that harnesses the benefits of IoT while addressing its inherent challenges. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of IoT devices, creating a brighter, more connected, and efficient world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)