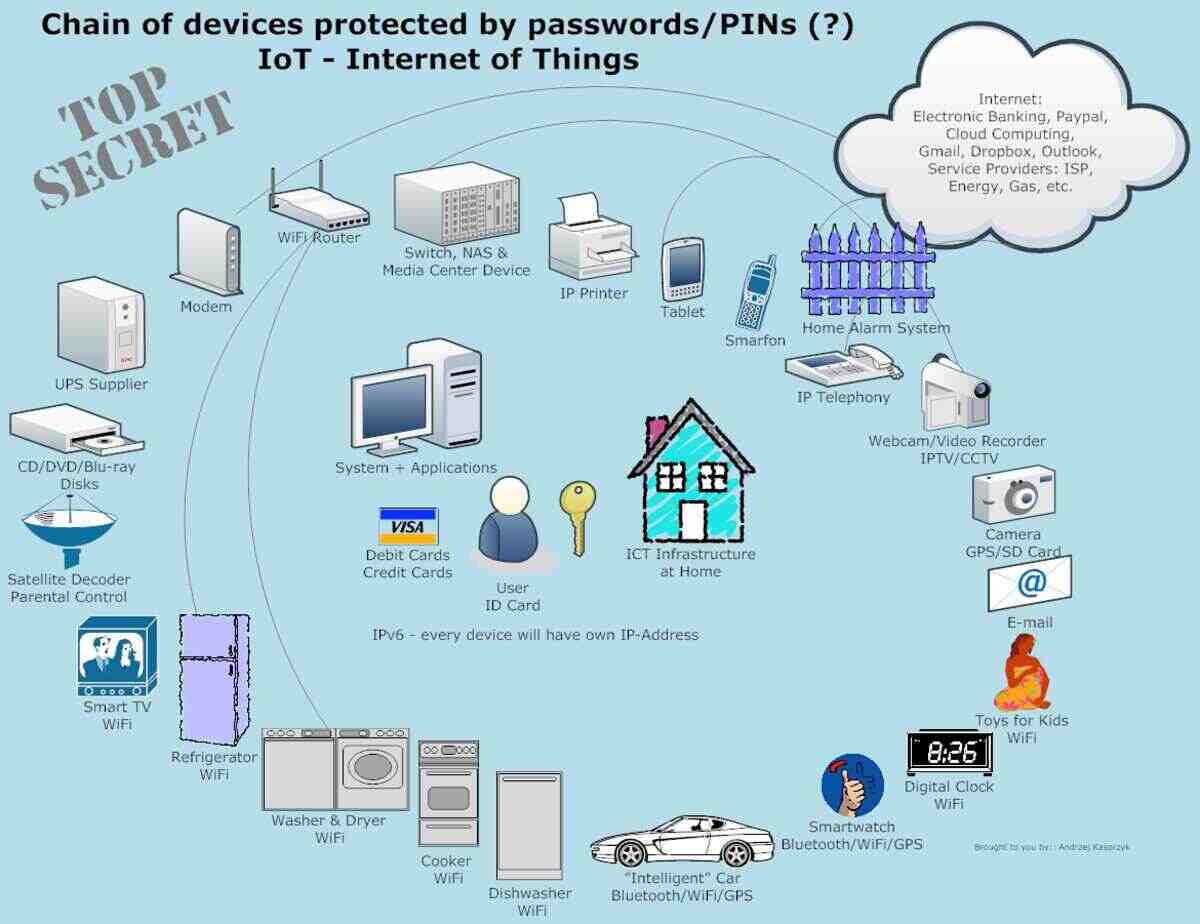
The Internet of Things (IoT) authorizes users to remotely control various aspects of their lives, enhancing convenience and efficiency in interacting with electronic equipment. However, effectively preventing and managing IoT devices can be challenging. This guide elucidates the principles of How TO Control IoT Devices, standard protocols, and a step-by-step process to follow.
How To Control IoT Devices and Management Work?
Controlling and managing IoT devices involves integrating interconnected smart devices within a network that can be monitored, controlled, and automated. Key functionalities in this process include:
Provisioning and Authentication
Provisioning entails setting up and configuring devices to join the network and function correctly. Authentication verifies the identity of an IoT device or user attempting to access the network or specific resources.
Configuration and Control
Devices and networks are dynamic, constantly evolving entities. Configuration enables devices to advance beyond initial provisioning, while remote control facilitates efficient and intelligent automation.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
Regular monitoring and diagnostics allow users to assess the performance of individual or multiple IoT devices. Users can obtain insights into general data, such as home temperature or vibration levels, and establish customized settings to trigger notifications for security breaches or device damage.
Software Maintenance & Updates
Daily software maintenance and updates are key for keeping IoT devices secure, reliable, and up-to-date with the latest features and improvements.
Common Ways of How To Control IoT Devices
Mobile Applications
Mobile apps are a prevalent and user-friendly method for controlling IoT Devices. Manufacturers typically provide dedicated apps, enabling users to manage device settings, monitor data, and execute commands remotely via intuitive interfaces on smartphones and tablets.
Voice Control
Voice-controlled assistants like Amazon Alexa & Google Assistant offer hands-free interaction with IoT devices. Voice control increases accessibility & convenience, making it ideal for smart home applications.
Web Interfaces
Web interfaces allow users to access a device’s control board through a web browser on their computer or mobile device. They offer similar functionalities to mobile apps and prove beneficial when away from home.
Remote Control Protocols
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and the CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) facilitate efficient data exchange between IoT devices & controllers, make suring secure & reliable connections.
NFC
Near-field communication (NFC) enables secure & efficient control through proximity interactions, suitable for industrial or healthcare settings.
Bluetooth & Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth & BLE provide short-range wireless communication between IoT devices & controllers, with BLE providing greater energy order for battery-powered devices.
Physical Controls
Physical controls, similar as buttons, switches, or touchscreens, offer a convenient way to manage IoT devices without relying on external controllers or networks.
List of IoT Device Management Platforms
Azure IoT Hub
Azure IoT Hub is a scalable cloud platform offering an IoT device registry, data storage, and robust security features, facilitating IoT application development.
Emnify
Emnify provides a cloud-based connectivity management platform with remote SIM provisioning, real-time data monitoring, secure Connectivity, and integration with various IoT applications.
Hologram
Hologram offers cellular SIM cards and a user-friendly monitoring dashboard, with flexible and affordable pricing plans for managing IoT devices.
AWS IoT Device Management
AWS IoT Device Management simplifies the onboarding, organization, monitoring, and updating of IoT devices at scale, ensuring secure and efficient management.
Exosite ExoSense IoT
ExoSense is a remote condition monitoring application that allows organizations to aggregate and visualize sensor data, receive timely alerts, and optimize processes.
Google Cloud IoT Core
Google Cloud IoT Core gives a fully managed service for secure connection, management, and data ingestion from globally dispersed devices.
Database Voyager
Voyager by Datablaze offers a versatile solution for efficiently managing IoT deployments. It features real-time IoT data dashboards and robust tracking capabilities.
IBM Watson IoT Platform
IBM Watson IoT Platform offers device registration, Connectivity, control, visualization, and storage of IoT data designed to facilitate the extraction of value from devices.
ArborXR
ArborXR manages AR & VR device fleets, enabling users to deploy content and updates remotely while controlling what others can see and do in the headset.
Controlling IoT Devices, A Step-By-Step Guide
Choose IoT Devices
Select IoT devices that suit your needs, similar as smart bulbs, plugs, thermostats, or speakers.
Setup IoT Hub
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to set up the IoT hub. The hub acts as a bridge between your devices & your smartphone or home network.
Connect IoT Devices
Follow specific instructions for each IoT device to connect to the hub or your home WiFi grid using the manufacturer’s mobile app or web interface.
Install Mobile App
Download and install the agreed mobile app for your IoT devices, which is available on iOS and Android platforms.
Create Accounts
Create accounts or sign in to the app using your credentials to sync your devices across multiple devices or access them remotely.
Pair, Name, and Group Devices
Pair each IoT device with the hub or smartphone, assign names for easy identification, and group devices based on rooms or functionalities.
Control and Test
Control and test your devices by turning on specific buttons and activating voice control, ensuring all devices respond correctly to commands.
Protocols for IoT Devices Remote Control & Management
MQTT
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol plan for low-bandwidth & unreliable networks. It is suitable for remote monitoring & telemetry.
CoAP
CoAP is designed for resource-constrained IoT devices in low-power networks, enabling efficient communication for IoT deployments with FINITE resources.
HTTP/HTTPS
Traditional web protocols like HTTP/HTTPS facilitate communication between web applications & IoT devices. They are often used in deployments with web servers or cloud platforms.
AMQP
AMQP supports robust message queuing & broker-based communication, making it suitable for complex IoT applications that require reliable communication & message processing.
DDS
DDS provides real-time communication & data distribution among IoT devices, commonly used in industrial IoT applications requiring high-performance & low-latency data exchange.
Challenges for How To Control IoT Devices
Interoperability Issues
Compatibility issues may arise in a diverse IoT ecosystem. Ensure device compatibility before making a purchase.
Connectivity Problems
Choose the right communication technology to avoid frequent disconnections. Improve network signal using WiFi extenders if necessary.
Data Privacy Concerns
IoT devices are at risk to cyberattacks. Regularly review privacy policies to understand data usage and storage.
Bonus Tips on How To Control IoT Devices on the Internet
Select the Right Communication Technology
Choose suitable communication technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Cellular, LPWAN, or Ethernet.
Configure Network Settings
Set up network parameters, similar as IP addresses, subnet masks, gateway addresses, and DNS servers, for proper device communication.
Security and Authentication
Implement secure authentication mechanisms, encryption, and communication protocols like TLS/SSL to protect devices and data.
Gateway or Hub Setup
Set up a gateway or hub to handle data aggregation, protocol translation, and cloud communication.
Internet Access Point
Ensure the local network where IoT devices are connected has Internet access, with the router or modem connected to the ISP.
Test and Monitor
Test communication capabilities to verify data transmission and implement monitoring solutions to track device performance.
Advanced Considerations for IoT Device Control and Management
While the basic steps & protocols provide a solid foundation for controlling IoT devices, more advanced considerations can further enhance an IoT ecosystem’s efficiency, security, & functionality.
Edge Computing
Edge computing require storing data closer to where it is generated rather than in a centralized cloud. This reduces latency, decreases bandwidth use, & permits for real-time data analysis and response. Implementing edge computing can be particularly beneficial in environments with time-sensitive applications or limited Connectivity.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) notably increase the capabilities of IoT devices by permit predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, & automation based on data designs. For instance, an AI-powered thermostat can learn a user’s preferences & adjust position autonomously for optimal comfort & energy efficiency.
Secure Communication Channels
Make Suring secure communication between IoT devices and their controllers is paramount. In addition to using encryption protocols like TLS/SSL, consider implementing VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) & private LTE networks for sensitive data transmission. Regularly update encryption methods to mitigate emerging security threats.
Robust Data Management
Managing the data generated by IoT devices need storage, processing, and analysis. Use scalable cloud storage solutions, make sure data integrity through regular backups, and leverage data analytics tools to extract actionable insights. Implement data lifecycle management policies to handle data from creation to deletion securely.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to regulatory standards similar as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability along with Accountability Act), & CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is essential for IoT deployments, especially those handling personal or sensitive data. Make Suring compliance by implementing stringent data protection measures & staying updated with regulatory changes.
Device Interoperability
Increasing interoperability by choosing IoT devices that adhere to standard communication protocols and frameworks like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread. This makes sure seamless integration & communication between devices and manufacturers, creating a more cohesive and flexible IoT ecosystem.
Scalability Planning
To accommodate future expansion of your IoT network, plan for scalability from the outset. This involves selecting platforms and devices that support scalability, implementing modular architectures, and ensuring your network infrastructure can handle increased data loads and device connections.
Redundancy and Failover Strategies
Implement redundancy & failover strategies to ensure continuous operation of your IoT system in case of device or network failures. This includes using backup devices, alternative communication paths, & disaster recovery plans to maintain functionality & data integrity during unforeseen events.
Energy Efficiency
Optimize energy consumption of IoT devices by utilizing low-power communication protocols similar to as BLE & LPWAN. Implement energy-efficient hardware & software solutions, & consider solar or other renewable energy sources for powering devices in remote or off-grid locations.
Future Trends in IoT Device Control and Management
5G Connectivity
The advent of 5G technology promises to revolutionize IoT with faster data speeds, lower latency, & greater Connectivity. This will allow more sophisticated & real-time applications similar to as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, & advanced industrial automation.
Blockchain for IoT Security
Blockchain technology gives a decentralized approach to securing IoT networks. By giving immutable & transparent transaction records, blockchain can increase security, trust, and traceability in IoT applications, particularly in supply chain management & financial transactions.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing, though still in its budding stages, holds the potential to transform IoT by solving complex problems much faster than classical computers. This could lead to cryptography, optimization, & machine learning breakthroughs, significantly increasing IoT capabilities.
Biometric Authentication
Integrating biometric corroborate methods, similar to as fingerprint or facial recognition, can enhance security & user convenience in IoT systems. This is especially relevant for personal & home automation devices, where ease of use & security are paramount.
Environmental Sensing and Sustainability
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, IoT devices with environmental sensors can monitor & manage energy usage, detect pollutants, and optimize resource consumption. This contributes to greener & more sustainable practices in many sectors, from agriculture to urban planning.
Conclusion
How To Control IoT Devices requires a comprehensive understanding of provisioning, configuration, monitoring, and maintaining these devices. By leveraging various control methods for How To Control IoT Devices, adhering to standard protocols, and utilizing advanced technologies, users can optimize their IoT ecosystems for enhanced efficiency, security, and functionality. As IoT keeps up to evolve, staying abreast of emerging trends & best practices will make sure IoT solutions’ successful & sustainable deployment.