In the modern age, Wireless Technology has evolved from a convenient innovation into the backbone of our connected society. It enables the transmission of data without biological cables, using electromagnetic waves to link billions of devices across the globe. From hospitals monitoring patients in real time to self-driving cars navigating city streets, the influence of this technology is felt in nearly every aspect of life.
This article explores the science behind wireless communication, its practical benefits, applications in different industries, challenges it faces, and the future trends shaping its development.
What Is Wireless Technology?
At its core, Wireless Technology refers to methods of transmitting data over distances without physical connections. It operates within the electromagnetic spectrum, which is divided into frequency bands allocated for specific uses — such as Wi-Fi, cellular, and satellite communications.
Two essential principles make it work:
- Signal Attenuation: Electromagnetic signals weaken as they travel. This natural drop in strength prevents devices operating on similar frequencies from interfering with each other.
- Spectrum Segmentation: The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into ranges for different services, providing organized, interference-free communication.
How Wireless Communication Works
Wireless communication is a coordinated process involving:
- Data Encoding: Knowledge is converted into electromagnetic signals.
- Transmission Medium: Signals travel via radio, microwave, or infrared surges.
- Reception: Devices decode the signals into usable data.
- Protocols: Standards like Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.3, and 5G ensure speed, security, and compatibility.
These elements combine to allow considerable devices to communicate simultaneously, whether they are meters apart or divided by continents.
Everyday Applications of Wireless Technology

The presence of wireless methods in our daily routines is so seamless that we often take them for granted. Examples include:
- Wi-Fi Networks: Supplying internet access in homes, workplaces, and public areas.
- Bluetooth Devices: Connecting headphones, speakers, wearables, and smart home gadgets.
- Cellular Networks: Supporting global voice, text, and data communication.
- Satellite Communication: Bringing connectivity to remote and rural areas.
- Smart Homes: Allowing centralized control of lighting, security, and appliances.
Advantages of Wireless Technology
Wireless connectivity offers benefits that have reshaped industries and lifestyles:
- Mobility & Flexibility: Stay connected from virtually anywhere.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for extensive wiring infrastructure.
- Scalability: Networks can be expanded to support more users and devices with minimal effort.
- Multi-Device Support: Manages high traffic without significant performance issues.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its strengths, wireless systems face certain hurdles:
- Signal Interference: Physical barriers and electronic contraptions can disrupt signals.
- Security Concerns: Without robust encryption, wireless communications can be intercepted.
- Spectrum Limitations: The finite electromagnetic spectrum must be managed efficiently to avoid congestion.
Wireless Technology in Different Sectors

1. Healthcare
Wireless solutions are revolutionizing healthcare delivery:
- Wearable Health Devices: Track vital signs such as heart rate and glucose levels in real time.
- Telemedicine: Enables remote consultations and diagnostics.
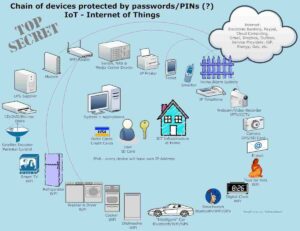
- Hospital IoT: Improves asset tracking, patient monitoring, and workflow efficiency.
Example: Remote cardiac monitoring devices can alert doctors instantly if a patient’s heart rhythm becomes irregular, enabling rapid intervention.
2. Industrial Automation
Manufacturing and industrial operations rely heavily on wireless systems:
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Connects machinery and sensors for data-driven decision-making.
- Predictive Maintenance: Identifies potential failures before they occur.
- Flexible Production: Allows easy reconfiguration of systems for different product lines.
3. Education
Wireless integration is transforming learning environments:
- Smart Classrooms: Use wireless displays, tablets, and interactive boards.
- E-Learning Access: Students can attend classes and access resources from anywhere.
- Collaborative Tools: Facilitate group projects and real-time content sharing.
4. Transportation & Logistics
Connectivity is critical for efficiency and safety:
- Fleet Management Systems: Optimize routes and reduce fuel consumption.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): Support vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
- RFID Tracking: Enhances supply chain visibility and inventory control.
5. Smart Cities
Urban development is increasingly dependent on wireless infrastructure:
- Connected Streetlights: Adjust lighting based on environmental conditions.
- Waste Management Sensors: Alert when bins need emptying.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracks air quality, temperature, and noise levels.
Quick Reference: Applications, Benefits & Challenges
| Application Area | Key Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Real-time patient monitoring, remote consultations, improved treatment accuracy | Data security, device compatibility |
| Industrial Automation | Predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, optimized production | Network reliability in harsh environments |
| Education | Interactive learning, remote access, resource sharing | Connectivity gaps in rural areas |
| Transportation & Logistics | Route optimization, reduced fuel costs, improved delivery accuracy | Signal interference, high deployment costs |
| Smart Cities | Energy efficiency, better resource management, environmental monitoring | Integration complexity, privacy concerns |
| Everyday Connectivity | Mobility, flexibility, multi-device support | Bandwidth congestion, cybersecurity threats |
The Future of Wireless Technology
The next decade promises groundbreaking advancements:
-
- 5G & Beyond: Delivers ultra-fast speeds, minimal latency, and massive device connectivity.
- Li-Fi: Uses light waves for high-speed, interference-free data transmission.
- Quantum Communication: Offers near-unbreakable encryption for sensitive data.
- AI-Powered Networks: Automatically adjust bandwidth, detect threats, and optimize performance.
Security & Privacy Measures
As reliance on wireless systems grows, so does the need for security:
- Encryption Protocols: Standards like WPA3 protect data in transit.
- Authentication: Multi-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access.
- Firmware Updates: Keep devices protected against new vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Wireless Technology is more than just a convenience — it’s the foundation of a connected, intelligent, and efficient world. By eliminating the constraints of cables, it has reshaped industries, empowered communities, and enabled innovations once thought impossible.
With the rise of 5G, Li-Fi, AI-driven networks, and quantum-secure communication, the future will see even greater integration of wireless systems into every corner of life. As these technologies mature, they will unlock possibilities that will transform how we live, work, and interact — making the world smarter, safer, and more connected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Wireless Technology?
Wireless Technology allows data to be transmitted through electromagnetic waves without the need for material cables, enabling devices to communicate seamlessly.
How does Wireless Technology work?
It works using regulated frequencies, transmitters, receivers, and communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G to send and receive data efficiently.
What are examples of Wireless Technology?
Common examples include Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, cellular networks, satellite communication, and RFID systems used in logistics and smart devices.
What is the future of Wireless Technology?
The future includes faster networks, enhanced security, AI-driven optimization, and emerging tech like 5G, Li-Fi, and quantum communication for seamless connectivity.
Why is Wireless Technology important?
It connects people and devices globally, drives innovation across industries, and supports modern infrastructure, making life more efficient and connected.